-
 UV11W High-efficiency Intelligent UV Water Sterilizer Cat:Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer
UV11W High-efficiency Intelligent UV Water Sterilizer Cat:Ultraviolet Water SterilizerThe UV11W High-efficiency Intelligent UV Water Sterilizer is an advanced water purification system that offers convenience and reliability. This steri...
See Details -
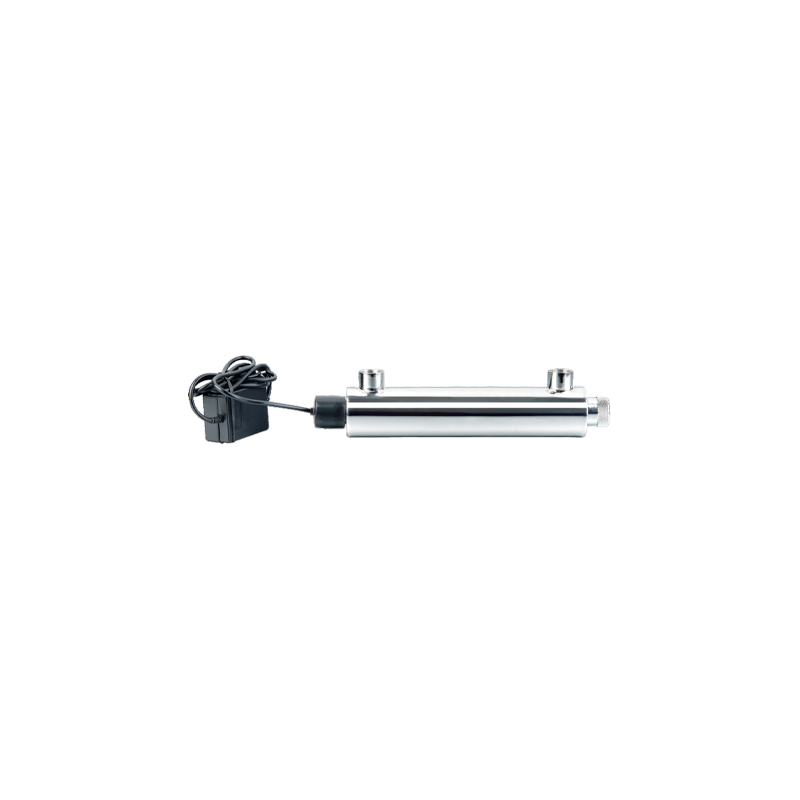 UV16W-A Household Stainless Steel UV Water Sterilizer Cat:Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer
UV16W-A Household Stainless Steel UV Water Sterilizer Cat:Ultraviolet Water SterilizerThe UV16W-A Household Stainless Steel UV Water Sterilizer is an innovative solution for ensuring safe and pure water in your home. Designed with durab...
See Details -
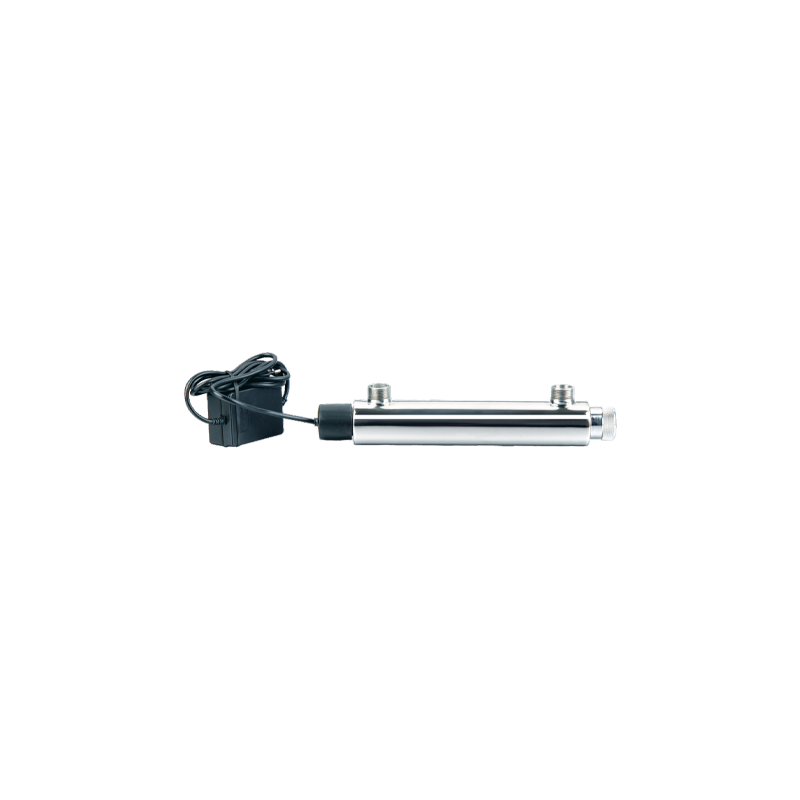 UV16W-B 304 Stainless Steel Water Purifier Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer Cat:Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer
UV16W-B 304 Stainless Steel Water Purifier Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer Cat:Ultraviolet Water SterilizerUV16W-B 304 Stainless Steel Water Purifier Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer is an efficient water treatment equipment based on advanced ultraviolet disinf...
See Details -
 UV25W Stainless Steel Ultrafiltration Pre-Filtration UV Sterilizers For Water Cat:Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer
UV25W Stainless Steel Ultrafiltration Pre-Filtration UV Sterilizers For Water Cat:Ultraviolet Water SterilizerUV25W Stainless Steel Ultrafiltration Pre-Filtration UV Sterilizers For Water uses high-quality stainless steel materials, which have superb corrosion...
See Details -
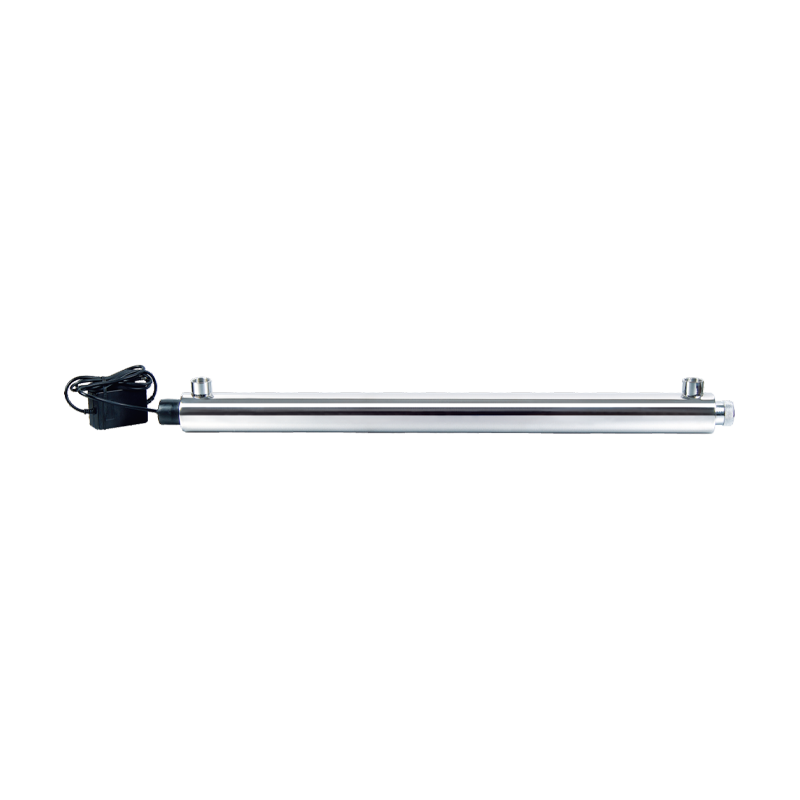 UV30W-55W Automatic Ultraviolet Sterilizer UV Filtration For Drinking Water Cat:Ultraviolet Water Sterilizer
UV30W-55W Automatic Ultraviolet Sterilizer UV Filtration For Drinking Water Cat:Ultraviolet Water SterilizerThe core advantage of UV30W-55W Automatic Ultraviolet Sterilizer UV Filtration For Drinking Water lies in its efficient and rapid disinfection capabil...
See Details -
 TQ-R03 Stainless Steel Booster Double Water Full Effect RO Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Ro System
TQ-R03 Stainless Steel Booster Double Water Full Effect RO Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Ro SystemTQ-R03 Stainless Steel Booster Double Water Full Effect RO Water Purifier is a household water purification device that combines efficient water purif...
See Details -
 TQ-R05 Multifunctional Water Purification Source RO Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Ro System
TQ-R05 Multifunctional Water Purification Source RO Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Ro SystemThe TQ-R05 Multifunctional Water Purification Source RO Water Purifier is an advanced, versatile water purification solution designed for households a...
See Details -
 TQ-R06 Stainless Steel Environmentally Friendly RO Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Ro System
TQ-R06 Stainless Steel Environmentally Friendly RO Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Ro SystemThe TQ-R06 Stainless Steel Environmentally Friendly RO Water Purifier combines advanced RO filtration technology, durable stainless steel housing, and...
See Details -
 Stainless Steel Pure Double Water Pipe Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Pipeline Water Purifier
Stainless Steel Pure Double Water Pipe Water Purifier Cat:Stainless Steel Pipeline Water PurifierThe Stainless Steel Pure Double Water Pipe Water Purifier is an advanced water purification system designed to provide dual-mode purified water with e...
See Details -
 TQ-R08 Stainless Steel High-Flow RO Water Filter Cat:Stainless Steel Ro System
TQ-R08 Stainless Steel High-Flow RO Water Filter Cat:Stainless Steel Ro SystemThe Stainless Steel High-Flow RO Water Filter (TQ-R08) provides a powerful and effective solution for purifying drinking water, combining advanced rev...
See Details
The Role of Reverse Osmosis (RO) Systems in Ensuring Clean Drinking Water
In an era where clean water access is more important than ever, the technology behind water purification systems plays a crucial role in safeguarding public health. Reverse Osmosis (RO) systems have emerged as one of the most reliable and effective methods for producing clean drinking water, particularly in areas where natural water sources are contaminated or difficult to access. These systems use a highly specialized filtration process to remove impurities and contaminants, ensuring the water is safe, clean, and suitable for consumption.
Content
What is Reverse Osmosis (RO)?
Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a water filtration process that removes unwanted particles, contaminants, and impurities from water by pushing it through a semi-permeable membrane. The membrane allows only water molecules to pass through, rejecting larger particles such as salts, minerals, bacteria, viruses, and other harmful substances.
RO systems operate under the principle of osmosis, which is the natural movement of solvent molecules from a region of low solute concentration to a region of high solute concentration through a semi-permeable membrane. Reverse osmosis, however, involves reversing this process by applying pressure to the water, forcing it to move from a region of high solute concentration to low solute concentration, effectively filtering out contaminants.
The result is purified water that is free from many of the harmful substances that can affect human health, making it an ideal solution for producing clean drinking water.
How RO Systems Work
The process of reverse osmosis involves several key steps, each of which contributes to the overall purification of the water:
Pre-Filtration:
Before the water enters the RO membrane, it usually passes through one or more pre-filters. These filters remove larger particles, such as sediment, chlorine, and other chemicals that could damage the RO membrane or reduce its efficiency. Pre-filtration is essential in ensuring that the RO system operates effectively over time and that the membrane remains intact.
Reverse Osmosis Membrane:
The core of the RO system is the semi-permeable membrane. This membrane has tiny pores that only allow water molecules to pass through, rejecting most contaminants, including dissolved salts, bacteria, heavy metals, and other impurities. The size of the membrane pores is critical to the system's ability to purify water efficiently. The filtered water, known as permeate, is collected on the other side of the membrane, while the contaminants are left behind and flushed out.
Post-Filtration:
After the water passes through the RO membrane, it typically goes through additional filters (e.g., activated carbon filters) to remove any remaining contaminants and improve taste. Some systems also include a UV (ultraviolet) sterilizer to kill any remaining bacteria or viruses.
Storage Tank:
In many residential RO systems, the filtered water is stored in a tank for later use. This ensures that clean water is available on demand. The system is usually designed to maintain water pressure, allowing the filtered water to flow freely when needed.
Drainage:
The contaminants and waste water (called brine) that are filtered out during the RO process are flushed out through a drain. The brine consists of concentrated salts, minerals, and other impurities that have been removed from the water.
Benefits of RO Systems for Clean Drinking Water
RO systems offer a range of benefits that make them an excellent choice for providing safe, clean drinking water. These include:
Effective Removal of Contaminants
One of the most significant advantages of RO systems is their ability to remove a wide range of contaminants from water. The RO membrane effectively filters out substances such as:
- Heavy metals (lead, arsenic, mercury, etc.)
- Chlorine and chloramines
- Nitrates and nitrites
- Fluoride
- Pesticides and herbicides
- Salts and dissolved solids
- Microorganisms (bacteria, viruses, cysts, etc.)
As a result, RO systems can produce water that meets or exceeds the standards for drinking water set by health organizations.
Improved Taste and Odor
RO systems also improve the taste and odor of water by removing chlorine, sulfur, and other chemicals that can cause unpleasant flavors. Many people living in urban areas with chlorinated tap water may find that the taste and odor of their water are undesirable. By using an RO system, these issues can be minimized, providing a better drinking experience.
Safe Drinking Water for Sensitive Populations
Certain groups of people, such as young children, pregnant women, the elderly, and those with weakened immune systems, are particularly vulnerable to waterborne diseases and contaminants. RO systems can help provide purified water that is free from harmful microorganisms and chemicals, ensuring it is safe for consumption by these sensitive populations.
Cost-Effective Long-Term Solution
While the initial investment in an RO system may be higher than traditional water filters, over time, RO systems can be more cost-effective. Bottled water, for example, is an ongoing expense, and the environmental impact of plastic waste is another concern. An RO system provides a long-term solution to water purification needs without the ongoing costs and environmental impact of bottled water.
Environmental Benefits
RO systems also contribute to environmental sustainability. By reducing the reliance on bottled water, RO systems help reduce plastic waste, which is a significant environmental issue globally. Moreover, they encourage the use of tap water, which is often a more environmentally friendly option than bottled alternatives.
RO Systems in Different Applications
While RO systems are widely known for their use in home drinking water purification, they have various other applications in industries where clean, purified water is essential:
Industrial and Commercial Use
RO systems are used extensively in industries such as pharmaceuticals, electronics, and food and beverage manufacturing, where high-purity water is required for production processes. These industries often require water that meets stringent quality standards to ensure the quality and safety of their products.
Desalination and Water Scarcity Solutions
In regions where fresh water is scarce, RO technology is also used for desalination, turning seawater into fresh, potable water. This application is particularly crucial in coastal areas and islands where access to freshwater sources is limited.
Aquariums and Fish Farms
RO systems are also used in aquaculture and aquariums to provide purified water for fish and other aquatic organisms. The high purity of RO water ensures that harmful chemicals and contaminants do not harm the delicate ecosystems within these environments.
Healthcare and Laboratories
In healthcare and research settings, water quality is of utmost importance. RO systems are used to provide ultrapure water for laboratories, medical devices, and even in the preparation of medications where water contamination could affect the outcomes.
Challenges and Limitations of RO Systems
While RO systems offer many benefits, there are a few challenges and limitations to consider:
Water Wastage
RO systems require a certain amount of water to operate, and for every gallon of purified water produced, several gallons of water are often discarded as waste (brine). This issue can be mitigated in some systems with more efficient filtration technologies or by using the waste water for non-potable purposes, such as irrigation.
Cost and Maintenance
The initial cost of purchasing and installing an RO system, as well as the maintenance costs, can be relatively high compared to other water filtration options. Regular replacement of filters and membranes is required to ensure that the system continues to perform efficiently. However, the long-term benefits often outweigh the initial investment.
Mineral Removal
While RO systems are excellent at removing harmful contaminants, they also remove beneficial minerals, such as calcium and magnesium, which are essential for human health. Some RO systems include mineralizers to add these minerals back into the water, but this feature may increase the system's complexity and cost.
The Future of RO Systems
As water quality continues to be a global concern, the demand for efficient and reliable water purification solutions will grow. Advances in RO technology are being made to improve efficiency, reduce waste, and lower costs. Future innovations in RO systems will likely focus on energy efficiency, sustainability, and integration with renewable energy sources to make water purification even more accessible and environmentally friendly.



 English
English 中文简体
中文简体